How Does a Two-Stroke Motor Work? Understanding the Simple Powerhouse
- Table of Contents
- How Does a Two-Stroke Motor Work? Understanding the Simple Powerhouse
- What Is a Two-Stroke Motor?
- Why Do Two-Stroke Engines Matter Today?
- What Are the Essential Components?
- How Does the Two-Stroke Cycle Work Step by Step?
- What Is Scavenging and Why Does It Matter?
- How Does Lubrication Work in a Two-Stroke?
- Two-Stroke vs Four-Stroke: Which Fits Your Job?
- Where Do We See Two-Stroke Motors in Real Life?
- How Do Ports, Timing, and Flow Shape Power?
- Cooling, Ignition, and Fuel Systems You Should Know
- Fuel, Oil, and Ratios: What Should You Mix
- Common Problems and Simple Care Tips
- The Future of Two-Stroke Engines
- Is a Two-Stroke Right for You
- Quick Reference Tables
- FAQ
- References
- Key Takeaways
You want simple power in a small package. A two-stroke motor gives you that. In this guide I show you how it works in clear steps. You will see the parts. You will see the cycle. You will see why people still love this simple powerhouse. If you use tools or bikes you will save time and avoid mistakes.
What Is a Two-Stroke Motor?
A two-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine. It turns fuel into motion in only two strokes of the piston. The piston goes up once. It goes down once. That’s one full two-stroke cycle. You get a power stroke every time the crankshaft makes one full turn. That is why a two-stroke feels strong for its size.
In a four-stroke engine you get power every two turns. In a two-stroke you get power every turn. This is the big two stroke vs four stroke operation difference. Two-strokes use ports in the cylinder instead of valves. The engine breathes and clears exhaust with smart port timing. The spark plug lights the fuel air mixture at just the right time.
Why Do Two-Stroke Engines Matter Today?
You see two-strokes in small engines that must stay light. Think chainsaw, weed trimmer, leaf blower, outboard motor, dirt bike, snowmobile, and even karting engine setups. These tools need speed, a high power to weight ratio, and simplicity of design.
Here is the Problem. You need a strong engine that is easy to fix. You want fewer parts. You want to carry less weight. You want to hold the tool at any angle. A traditional engine can feel heavy and complex.
Now the Agitate. A heavy engine wears you out. A complex engine costs more. It can slow your work. It can fail when you tilt it or rush the job.
Here is the Solution. A two-stroke engine is compact, has less moving parts, and gives quick throttle response. It can run sideways or upside down. You mix oil into the gas for lubrication. You do not need a heavy oil pump or a big sump. For many jobs the two-stroke is the right call.
What Are the Essential Components?
A two-stroke motor keeps parts simple. The magic sits in how they work together.
- Piston and piston ring seal the combustion chamber and slide in the cylinder.
- Connecting rod links piston to crankshaft to turn up-down motion into spin.
- Spark plug fires the mix.
- Carburetor blends fuel and air in many small engines. Some use direct fuel injection (DFI).
- Intake port, transfer port, and exhaust port manage gas flow.
- Reed valve or rotary valve can control intake.
- The crankcase holds the fresh charge before it moves up through the transfer port.
- The muffler and exhaust system guide and tune the flow out.
- An air filter protects the carburetor.
Here is a simple table that maps parts to jobs.
| Component | What it does |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | Houses two-stroke engine parts and forms the hot combustion chamber |
| Piston & Piston Ring | Seal the top, control piston movement in two stroke, sweep ports |
| Connecting Rod & Gudgeon Pin | Link piston to crank, pivot at the pin |
| Crankshaft & Flywheel | Turn power into rotation, smooth the crankshaft rotation 2 stroke |
| Spark Plug & Ignition System | Time the spark plug ignition two stroke at TDC |
| Carburetor or DFI | Meter fuel, mix air, or inject with direct injection two stroke |
| Reed Valve or Rotary Valve | Control intake flow and fuel induction system |
| Intake/Transfer/Exhaust Ports | Handle intake and exhaust in one revolution |
| Crankcase | Acts as pump for crankcase compression |
| Muffler & Exhaust | Shape exhaust system 2 stroke and sound |
If your tool includes a charging system you will also see a magneto or small alternator with a tiny stator and rotor. Learn how they pair in this clear guide on stator and rotor basics.
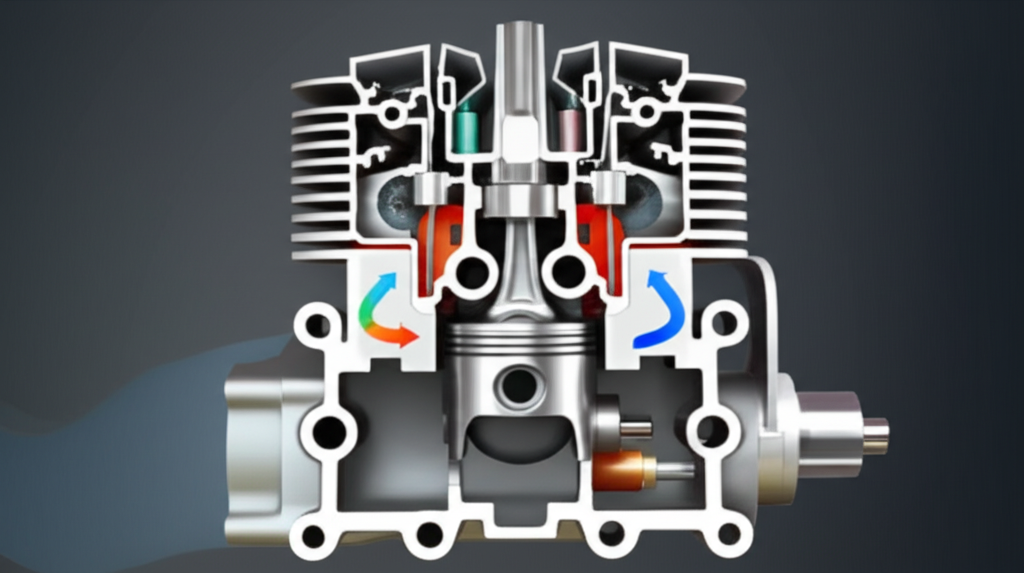
How Does the Two-Stroke Cycle Work Step by Step?
I like to picture the two-stroke cycle as a dance. The piston moves up and down. Ports open and close. Fresh charge comes in. Burned gases leave. You get power every turn. Here’s the engine cycle explanation.
- Stroke 1: Piston moves up. You get compression above the piston and intake below.
- Stroke 2: Piston moves down. You get power & exhaust/scavenging above and crankcase compression below.
Let’s break it down.
- Upward stroke (compression and power): Fresh mix enters the crankcase through the intake port. The reed valve shuts as the piston rises. Above the piston the fuel air mixture compresses. Near Top Dead Center (TDC) the spark plug fires. The power stroke definition 2 stroke is the push down after that flame front hits.
- Downward stroke (power and exhaust): Hot gas pushes the piston down. The exhaust port function starts when the piston uncovers the exhaust. Burned gas begins to leave. Then the transfer port operation comes in. Fresh charge rushes from the crankcase to the cylinder. This is the scavenging process in 2 stroke. Fresh mix pushes out the rest of the exhaust. The piston skirt function and port edges guide the flow.
That’s the whole two stroke cycle explanation. One up. One down. One power hit per turn.
What Is Scavenging and Why Does It Matter?
Scavenging is the sweep out of old gases and the fill with fresh mix. Good scavenging gives clean burn. Bad scavenging can waste fuel.
When the transfer port opens the pressure differential 2 stroke drives the fresh charge in. The port shape and cylinder port design aim the stream. The stream loops up and across. It pushes the burned gases out the exhaust port. This is how the engine breathes without valves.
Some fresh mix can slip out with the exhaust. That hurts fuel efficiency two stroke and raises emissions from two stroke engines. Port timing and shapes fight that loss. Tuned pipes help too.
How Does Lubrication Work in a Two-Stroke?
A two-stroke has no oil pan. There is no oil pump. So how do parts stay wet
You mix oil into the gas. We call this oil mixing for two stroke engines. The oil rides with the air and fuel. It coats the piston, piston ring, cylinder, connecting rod, and crankshaft. We call that mist lubrication. The lubrication system two stroke is simple and light.
Common gas oil mixture ratio values run from 25:1 to 50:1 for older gear. Many new tools use 40:1 to 50:1 with engine oil that is made for two-strokes. Some systems use direct oil injection. Always read your small engine repair and user guide. Get the mix right so you avoid wear and smoke.
Two-Stroke vs Four-Stroke: Which Fits Your Job?
You want a quick two-stroke vs four-stroke operation primer. Here it is. Two-strokes fire every turn. They use ports not valves. You mix oil in the gas. Four-strokes fire every two turns. They use valves with cams. They have a pump and dedicated oil sump.
Here is a clear table.
| Feature / Metric | Two-Stroke Engine | Four-Stroke Engine | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power-to-Weight Ratio | Higher due to power every revolution | Lower per cc | Great for tools and bikes |
| Mechanical Complexity | Simpler with fewer moving parts | More complex with valves and cams | Lower cost and easy fix |
| Lubrication System | Pre-mix fuel & oil or oil injection | Oil sump with pump | Oil in fuel can add smoke |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower due to scavenging loss | Higher | DI two-strokes improve a lot |
| Emissions | Higher in traditional designs | Lower | DI helps two-strokes meet rules |
| Torque Characteristics | Often peaky at higher RPMs | Flatter curve | Porting shapes the band |
| Operating Orientation | Any orientation | Usually fixed | Great for handheld use |
| Durability/Lifespan | Often shorter | Often longer | Depends on care and load |
| Market Trend | Niche but strong | Dominant in many areas | Rules shape the mix |
| Cost | Often lower | Often higher | Simpler build saves cost |
If you want to see how electric motors differ too read about the motor principle so you can compare engine vs motor basics.
Where Do We See Two-Stroke Motors in Real Life?
I first learned on a model aircraft engine. It screamed at high RPM two stroke engines and taught me respect. Later I tuned a dirt bike engine operation setup. That hit of power in the powerband hooked me. You may know the sound too. The sound of a two stroke engine is sharp and high. It has a snappy throttle response.
You can spot two-strokes in lawn and garden equipment engines like chainsaw, leaf blower, and weed eater engine function tools. Outboard motor two stroke designs still hold a place on lakes. Some snowmobile engine 2 stroke machines run in cold with air cooled 2 stroke engine or water cooled 2 stroke engine setups. Go-karts, RC engines, and older motorcycles love the high power to weight ratio and simplicity of design.
How Do Ports, Timing, and Flow Shape Power?
Port timing acts like the engine’s schedule. Port timing two stroke sets when ports open and close. That timing shapes engine breathing two stroke and the torque characteristics 2 stroke. It also sets the specific output 2 stroke and engine horsepower 2 stroke feel.
- A piston port engine design uses the piston to open and close the intake port.
- A reed valve operation lets air in when the crankcase volume 2 stroke drops.
- A rotary valve 2 stroke uses a disk to time intake.
You can even add a supercharger 2 stroke or turbocharger 2 stroke in special designs. That boosts thermal efficiency 2 stroke and power. It needs skill to tune. Porting, pipe length, and pressure differential 2 stroke all work together.
Cooling, Ignition, and Fuel Systems You Should Know
Small two-strokes use air cooled 2 stroke engine fins. Bigger ones may use water cooled 2 stroke engine jackets. Cooling helps engine reliability 2 stroke. It fights vibration 2 stroke engine stress and keeps mechanical efficiency 2 stroke high.
The ignition system 2 stroke uses a spark plug and coil. Many small tools use a magneto under a flywheel. Those tiny alternators use metal cores. If you build or fix alternators you will care about the quality of electrical steel laminations because the right steel lowers heat and keeps sparks strong.
Most small two-strokes use a carburetor function 2 stroke setup. Some high-end marine systems use direct injection two stroke to cut emissions and boost fuel efficiency two stroke. Examples include Evinrude E-TEC and Mercury OptiMax systems. They spray fuel after most exhaust leaves which reduces loss of the fresh charge.
Fuel, Oil, and Ratios: What Should You Mix
Use clean gasoline with the right octane rating for your engine. Mix in engine oil rated for two-stroke use. Most tools list the right gas oil mixture ratio. Follow it so the lubrication works. Too little oil causes wear. Too much oil makes smoke and fouls the spark plug.
Two-strokes burn oil with the fuel. That is why older gear shows more emissions from two stroke engines like hydrocarbons, CO, and PM. New emissions control rules push makers to cleaner designs like direct injection two stroke. That can improve specific fuel consumption 2 stroke and thermal efficiency.
Common Problems and Simple Care Tips
Let’s use PAS again.
- Problem: The engine bogs or will not start.
- Agitate: Your job stops. Your arm aches. You pull the cord and nothing happens.
- Solution: Check fuel, mix, air filter, spark plug, and carburetion basics first.
Here are common small engine mechanics two stroke checks.
- Bad mix or old fuel hurts engine reliability 2 stroke. Drain and refill.
- A clogged air filter starves the fuel induction system. Clean or swap it.
- Fouled spark plug kills the ignition system 2 stroke. Replace it.
- Worn piston ring or piston can drop compression. You may need an engine rebuild two stroke.
- Leaky reed valve or bad crankcase seals upset crankcase compression.
If you maintain gear for a fleet you may also manage generators and motors. When you need laminated cores for those machines you can explore high quality motor core laminations so your electric gear runs cool and lasts longer.
The Future of Two-Stroke Engines
Will two-strokes fade No. They will stay strong in niche applications where weight and simplicity win. We already see future of two stroke engines work with direct injection two stroke. It keeps power yet lowers emissions and raises fuel efficiency. Clean fuels and smarter control will help.
Many call the two-stroke a simple two stroke diagram come to life. That is true. Makers improve port timing two stroke with engine design tools and two stroke engine animation software. Some designs even try supercharger 2 stroke ideas. Others use tuned pipes and better muffler shapes to run cleaner and quieter.
If you also handle electronics at your shop you may use transformers and cores. Our partners serve that side too with core lamination stacks, silicon steel laminations, crgo lamination core, crngo lamination, ei core, ui lamination core, and transformer lamination core products. Visit their home base at core lamination stacks to explore.
Is a Two-Stroke Right for You
Ask yourself a few things.
- Do you need a compact engine design with high power to weight ratio and ease of manufacture 2 stroke for low cost of 2 stroke engine
- Will you run at many angles or carry the tool all day
- Do you accept oil consumption & smoke and some engine noise 2 stroke
If yes then pick a two-stroke. If you want the lowest environmental impact 2 stroke you may pick a four-stroke or a DI two-stroke. Each job is different so match the engine to the need.
Quick Reference Tables
Here is a simple guide that puts many ideas in one place. It will help you explain the two stroke engine principle to a friend.
The Two Strokes at a Glance
| Stroke | Above Piston | Below Piston | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up (Compression & Power) | Compress mix in the combustion chamber 2 stroke then fire at TDC | Intake of fresh charge into crankcase | Intake closed by reed valve or piston |
| Down (Power & Exhaust/Scavenging) | Expand hot gas and open exhaust port then transfer port | Crankcase compression of next charge | Exhaust then transfer open |
Two-Stroke Vocabulary You Will Hear
| Term | Simple meaning |
|---|---|
| how 2 stroke engine works step by step | The cycle of up stroke and down stroke |
| engine cycle explanation | How intake, compression, power, and exhaust happen |
| intake and exhaust in one revolution | Why two-strokes make power every turn |
| fuel air mixture in 2 stroke | Gas and air blend that burns |
| scavenging process in 2 stroke | Fresh mix pushes out exhaust |
| piston movement in two stroke | Up and down motion that runs the cycle |
| crankcase compression | Pressures the fresh mix under the piston |
| transfer port operation | Path of fresh charge into the cylinder |
| exhaust port function | Exit for burned gas |
| spark plug ignition two stroke | Spark at the right time |
| carburetor function 2 stroke | Mixes air and fuel |
| reed valve operation | One-way door for intake |
| rotary valve 2 stroke | Disk that times intake |
| piston port engine design | Piston edge runs intake timing |
| combustion chamber 2 stroke | Space where mix burns |
| piston skirt function | Helps cover and uncover ports |
| connecting rod two stroke | Joins piston to crank |
| crankshaft rotation 2 stroke | One turn per power stroke |
| cylinder port design | Shapes flow and power |
| two stroke engine animation | Shows the flow and timing |
| beginner’s guide two stroke | This article in simple words |
| how to maintain 2 stroke engine | Basic care and checks |
| common 2 stroke engine problems | Flooding, fouled plugs, air leaks |
| fuel efficiency two stroke | How far you go per fuel |
| power output 2 stroke engines | How much work you get |
| torque characteristics 2 stroke | How the pull feels across RPM |
| emissions from two stroke engines | HC, CO, and PM due to oil and loss |
| history of two stroke engines | Long use in bikes and tools |
| future of two stroke engines | DI, better ports, cleaner burn |
| direct injection two stroke | Fuel sprayed after exhaust leaves |
| engine rebuild two stroke | New rings, bearings, or top end |
| igniter two stroke | Spark system parts |
| cooling system two stroke | Air or water keeps temps down |
| air cooled 2 stroke engine | Fins on the cylinder |
| water cooled 2 stroke engine | Liquid jacket and pump |
| sound of a two stroke engine | High pitched and sharp |
| engine timing 2 stroke | When spark and ports act |
| supercharger 2 stroke | Blower to add air |
| turbocharger 2 stroke | Exhaust-driven boost |
| performance tuning 2 stroke | Porting and pipes to gain power |
| gas oil mixture ratio | The number like 40:1 |
| two stroke engine parts diagram | Map of the parts |
| engine horsepower 2 stroke | Power rating |
| engine displacement 2 stroke | Size in cc |
| specific fuel consumption 2 stroke | Fuel per power unit |
| engine weight two stroke | How much it weighs |
| compact engine design | Small yet strong |
| high power to weight ratio | Lots of power for its size |
| simplicity of design | Few parts and easy build |
| less moving parts 2 stroke | No valves or cams |
| fuel induction system | How air and fuel get in |
| ignition system 2 stroke | Spark parts and timing |
| exhaust system 2 stroke | Pipe and muffler |
| crankcase volume 2 stroke | Space under the piston |
| pressure differential 2 stroke | Push that moves the charge |
| intake charge flow | Movement of fresh mix |
| fresh charge vs exhaust gases | Clean mix and burned gas paths |
| engine breathing 2 stroke | How the engine inhales and exhales |
| port timing two stroke | When ports open and shut |
| piston speed 2 stroke | How fast the piston travels |
| RPM two stroke engines | Revolutions per minute |
| thermal efficiency 2 stroke | How well heat turns to work |
| mechanical efficiency 2 stroke | How the parts waste or save power |
| specific output 2 stroke | Power per liter or cc |
| engine noise 2 stroke | How loud it is |
| vibration 2 stroke engine | Shakes from firing each turn |
| throttle response 2 stroke | How fast the engine reacts |
| engine reliability 2 stroke | How long it stays strong |
| cost of 2 stroke engine | What you pay |
| ease of manufacture 2 stroke | How fast you can build it |
| environmental impact 2 stroke | What it does to air quality |
| small engine repair | Fixing small two-strokes |
| marine engine types | Outboards and more |
| lawn and garden equipment engines | Tools you use at home |
| dirt bike engine operation | How off-road bikes run |
| karting engine 2 stroke | Go-kart power units |
| model aircraft engine | Small glow engines |
| snowmobile engine 2 stroke | Cold weather power |
| two cycle engine working | Another name for two-stroke |
| how does gas get into 2 stroke engine | Through intake with reed or rotary valve |
| how does oil lubricate 2 stroke | Mixed with fuel as mist |
| what makes a 2 stroke powerful | Power each turn and low weight |
Entities and What They Mean in Use
| Entity | Where it fits |
|---|---|
| Piston, Cylinder, Crankshaft, Connecting Rod | Core reciprocating engine parts |
| Spark Plug, Ignition System | Light the charge |
| Carburetor, Carburetion | Fuel mix in small engines |
| Crankcase | Pumps fresh mix |
| Transfer Port, Exhaust Port, Intake Port | Port-based breathing |
| Reed Valve, Rotary Valve | Intake control |
| Combustion Chamber | Where it burns |
| Lubrication (Premix Oil) | Oil in the fuel |
| Exhaust System, Muffler | Gases flow out |
| Power Stroke, Compression Stroke, Expansion Stroke | Motion phases in the two-stroke cycle |
| Two-Stroke Cycle, Four-Stroke Engine | Engine families |
| Chainsaw, Outboard Motor, Motorcycle, Leaf Blower, Weed Trimmer | Common tools |
| Internal Combustion, Otto Cycle (modified) | The science |
| Piston Ring, Gudgeon Pin, Flywheel | Key hardware |
| Air Filter, Fuel Tank | Support parts |
| Engine Oil, Gasoline, Octane Rating | Fuel and lube |
| Emissions Control, Direct Fuel Injection (DFI) | Clean-up tech |
| Engine Cooling (Air/Water), Marine Propulsion | Keeping it cool and moving |
| Small Engines, High-Performance Engines, Engine Design | Types and focus |
| Torque, Horsepower | Output measures |
If you design or maintain small alternators for tools or boats you will care about the cores inside. You can review quality specs and options for motor core laminations to keep your electric parts efficient and cool.
FAQ
- Why do two-strokes feel so strong for their size
They make a power stroke every turn so they deliver more hits per minute for the same RPM.
- Do I need special oil
Yes. Use two-stroke engine oil that mixes with gasoline. Follow your oil mixing ratio.
- Why do some two-strokes smoke
They burn oil with fuel. Too rich a mix or a cold engine makes more smoke.
- Can a two-stroke be clean
Yes. Direct injection two stroke and smart porting cut emissions and can rival some four-strokes.
- What breaks first
On hard use the piston ring or top end wears first. Good mix and filters help a lot.
References
- Small Engine Repair Manuals and Manufacturer User Guides
- Environmental Protection Agency reports on nonroad spark-ignition engines
- Engineering Textbooks on Internal Combustion Engines and the Modified Otto Cycle
- Marine Engine Reviews on DI systems such as Evinrude E-TEC and Mercury OptiMax
- Motorcycle Industry Articles on Two-Stroke Porting and Powerbands
Key Takeaways
- A two-stroke completes its two-stroke cycle in one turn so you get one power stroke per revolution.
- Ports run intake, transfer, and exhaust so there are less moving parts and a simpler design.
- Mixing oil into fuel gives simple lubrication yet adds emissions and smoke.
- Two-strokes shine in tools and sports where high power to weight ratio and compact engine design matter most.
- You can manage common 2 stroke engine problems with fresh fuel, clean filters, and a good plug.
- Modern direct injection two stroke can boost fuel efficiency and cut emissions while keeping snap.
- Match the engine to the job so you get the right mix of power, weight, cost, and care.