What is a Squirrel Cage Fan? Your Essential Guide to This Unseen Hero
Ever wonder what that gentle hum is when your furnace kicks on? Or the whirring sound from your air conditioner that brings sweet relief on a hot day? Chances are, you’re hearing a squirrel cage fan in action. These amazing devices are everywhere, quietly moving air to keep us comfortable. But if one breaks down, you’ll notice it right away. This guide will show you everything you need to know about these workhorses of the air world.
Table of Contents
So, What Exactly is a Squirrel Cage Fan?
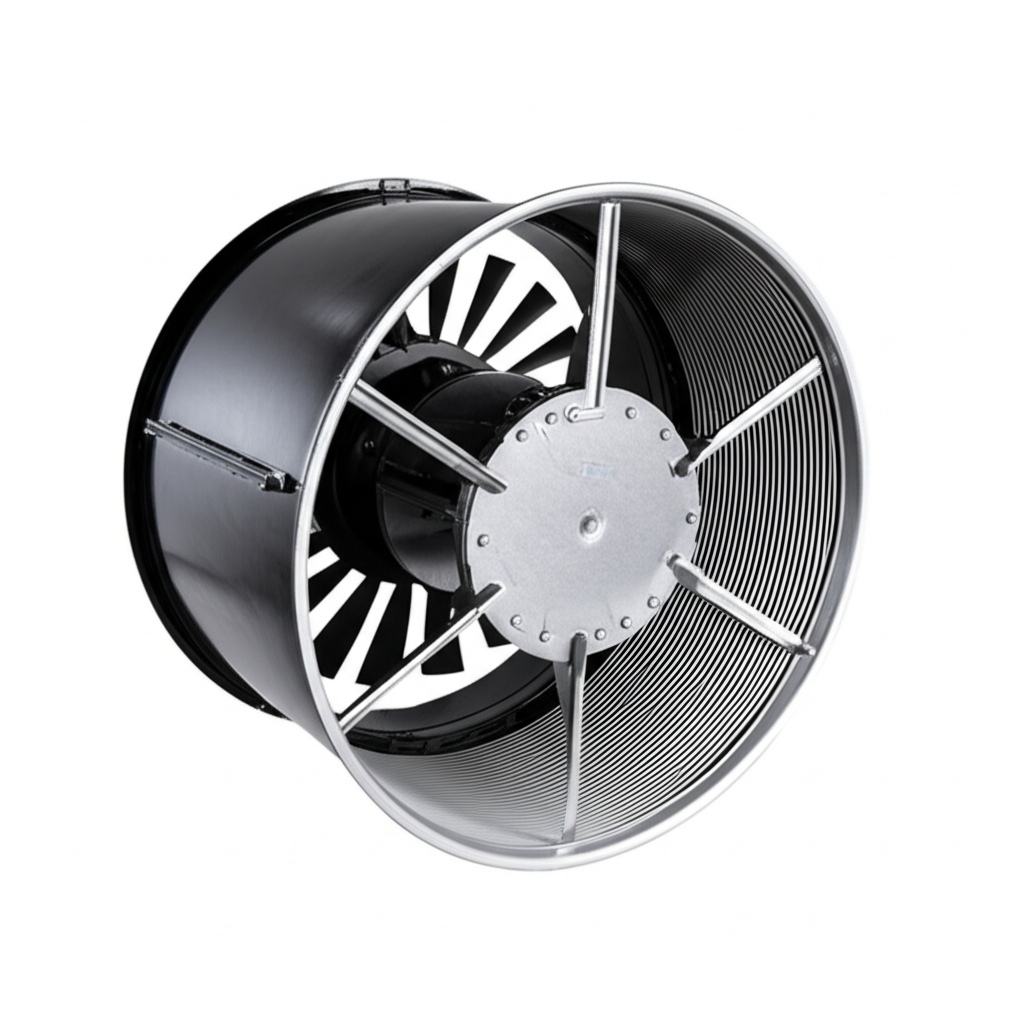
Let’s get right to it. A squirrel cage fan is a type of centrifugal fan. Now, that might sound technical, but the idea is simple. Instead of pushing air straight forward like a regular desk fan (that’s called an axial fan), a centrifugal fan pulls air in through the center and then flings it outwards at a 90-degree angle. It’s like a spinning water wheel, but for air.
This design is what makes it a powerhouse for many applications. It’s not just about creating a breeze; it’s about building pressure. If your air has to travel through long pipes or thick filters, you have a problem. Not all fans can handle that resistance. This is where the squirrel cage fan shines. It’s designed to overcome that static pressure and keep air moving, even when it has to push through the complex maze of your home’s ductwork. That’s why it’s a key part of most HVAC systems.
Why Is It Called a “Squirrel Cage”?
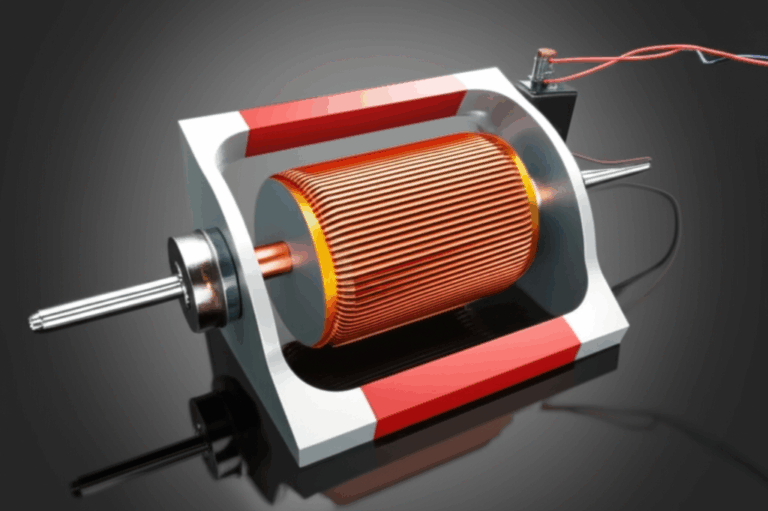
You might be picturing a tiny rodent running in a wheel, and you’re not far off! The heart of this fan is a spinning part called an impeller. This impeller is made of many small, forward-curved blades arranged in a circle, looking very much like a hamster or squirrel exercise wheel.
This unique impeller design is what gives the fan its name. Unlike a propeller-style fan with a few large blades, the squirrel cage fan has dozens of little blades. This design is fantastic for scooping up a lot of air in a small space and pushing it out with force. So, while there are no actual squirrels involved, the name perfectly describes the look of its most important part.
How Does It Work? The Science of Moving Air
Understanding how a blower works is all about understanding centrifugal force. It’s the same force that keeps water in a bucket when you swing it over your head or pushes you to the side on a fast merry-go-round.
Here’s the step-by-step process:
This constant process creates a steady and powerful airflow volume, making it perfect for applications that need consistent air delivery against resistance.
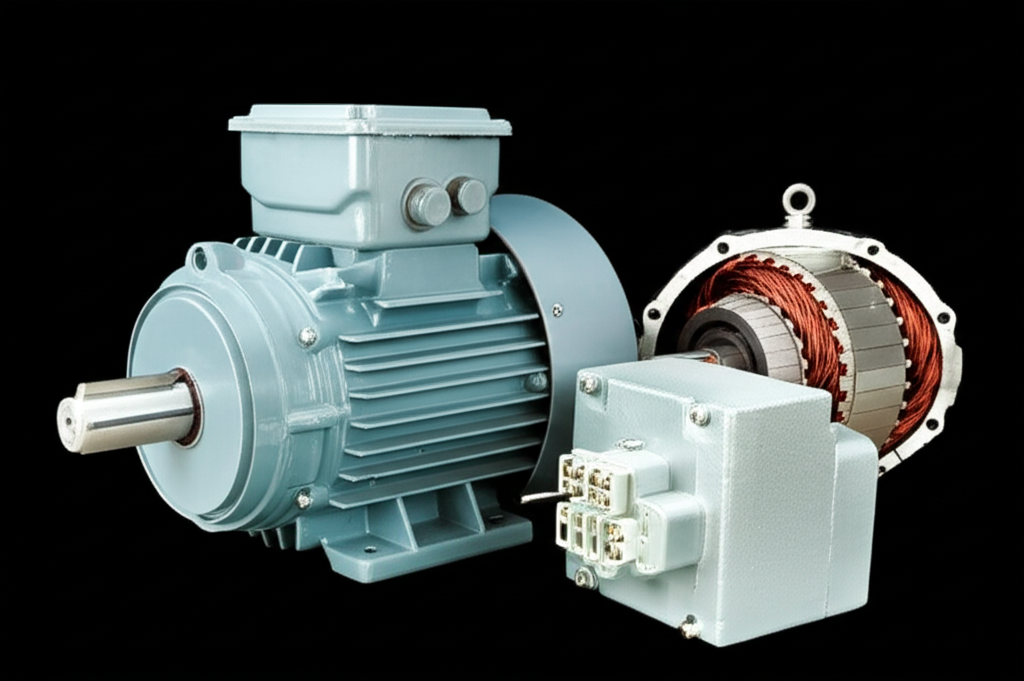
A Look Inside: What Are the Parts of a Centrifugal Fan?
A squirrel cage fan might seem complex, but it’s made of just a few key parts working together. Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting and maintenance.
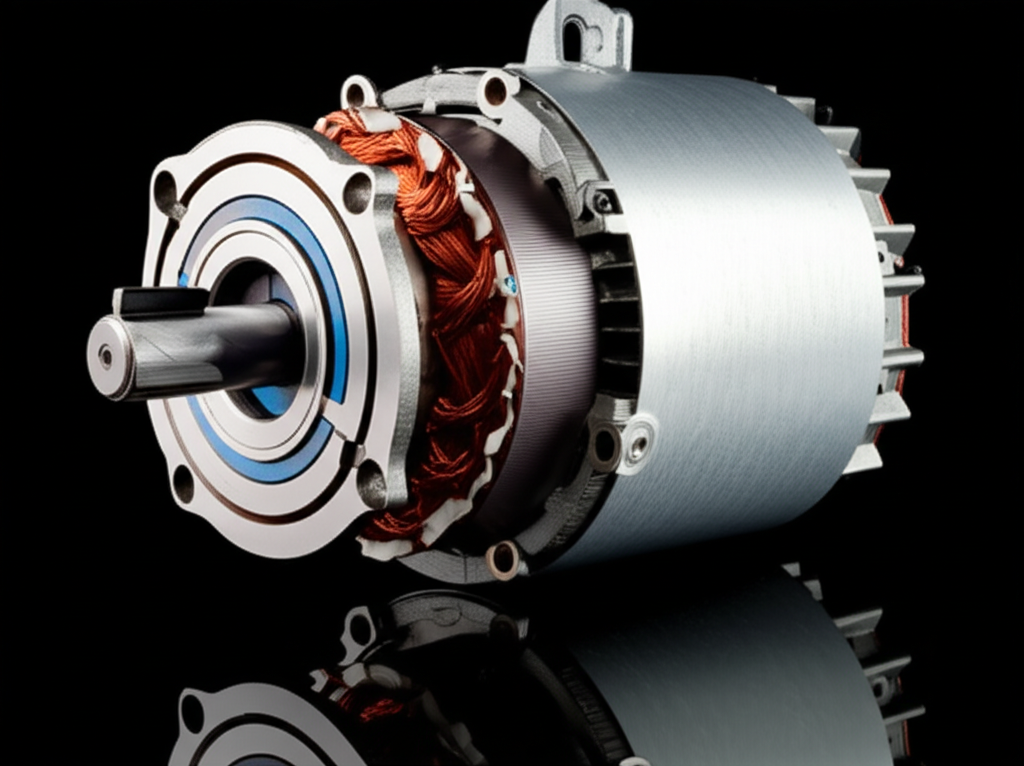
- Impeller (or Wheel): This is the “squirrel cage” itself. It’s a drum-shaped wheel with many small, forward-curved blades around its edge. The quality of the impeller material, often steel or aluminum, determines its durability and service life.
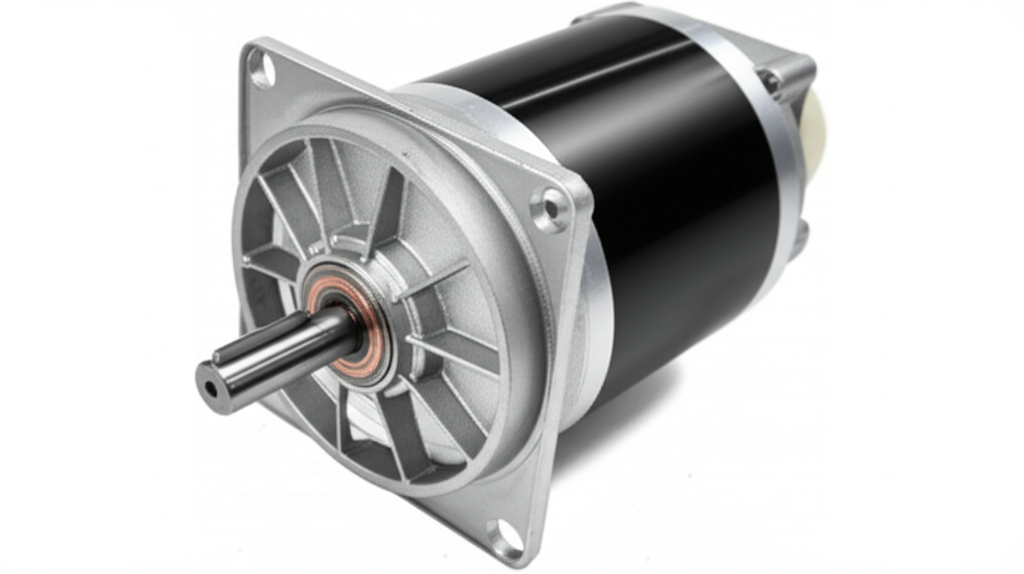
- Motor: This is the engine of the fan. The fan motor horsepower determines how powerful the fan is. It can be an AC motor or a more efficient DC motor. The motor turns a shaft, which in turn spins the impeller. The heart of the motor relies on quality components like electrical steel laminations to ensure efficiency and reduce energy loss.
- Housing (Casing or Volute): This is the shell that encloses the impeller. Its snail-like shape is designed to efficiently collect the air thrown off by the impeller and direct it out of the fan’s discharge opening. The housing material can range from plastic in small appliances to heavy-gauge steel in industrial blowers.
- Drivetrain: This connects the motor to the impeller. In a direct drive setup, the impeller is mounted right on the motor’s shaft. In a belt drive system, a belt and pulleys connect the motor to the impeller, which allows for more flexible speed adjustments. The internal mechanics, including the relationship between the stator and rotor, dictate the fan’s power and efficiency.
Where Can You Find These Fans in Plain Sight?
You’d be surprised how often you come across a squirrel cage blower. Their ability to move air efficiently in tight spaces makes them incredibly versatile.
Residential Applications:
- Furnaces and Air Conditioners: The main blower in your home’s HVAC system is almost certainly a squirrel cage fan. It’s the muscle that pushes warm or cool air through every vent.
- Kitchen Exhaust Hoods: That fan above your stove pulling smoke and smells away? That’s a squirrel cage fan, working hard against the resistance of a grease filter.
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans: These small fans are designed to move moist air out through ductwork, preventing mold and mildew.
- Hair Dryers: Yes, even that little handheld device uses a tiny squirrel cage fan to create a powerful stream of air.
Commercial and Industrial Applications:
- Commercial Ventilation Systems: Large buildings use massive air handling units (AHUs) with powerful squirrel cage fans to circulate air throughout the entire structure.
- Fume Extraction Systems: In places like welding shops or science labs, these fans are crucial for removing harmful fumes and dust.
- Electronics Cooling: High-power electronics and server racks use them to prevent overheating.
- Industrial Processes: They’re used for everything from drying grains to blowing air into industrial furnaces.
Are Squirrel Cage Fans the Best Choice? Pros and Cons
Like any piece of technology, squirrel cage fans have their strengths and weaknesses. The key is choosing the right fan for the right job.
Advantages:
- Great with Pressure: Their main benefit is the ability to generate high static pressure. This makes them perfect for systems with extensive ductwork, filters, or other obstructions.
- Compact Size: They can move a lot of air for their size, which is why they fit so well inside furnaces and air conditioners.
- Stable Airflow: They provide a consistent and predictable airflow volume, which is important for heating and cooling systems.
- Quiet Operation: At lower speeds, they are often quieter than other fan types that move a similar amount of air, which is a big plus for residential heating and cooling.
- Cost-Effective: They are generally less expensive to manufacture than other high-pressure fans.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Efficiency: The fan static efficiency of a squirrel cage fan (typically 50-70%) is generally lower than that of its cousin, the backward-curved fan. This means they can use more energy to move the same amount of air.
- Prone to Dirt: The shape of the forward-curved blades can cause dust and grease to build up. This buildup can reduce airflow, increase energy consumption, and create vibration issues.
- Overload Risk: A unique quirk of these fans is that if the static pressure in the system drops too much (like if a large access panel is left open), the fan will try to move more air, causing the motor to draw more power and potentially overload.
How Does It Compare to Other Fan Types?
To really understand what makes a squirrel cage fan special, it helps to compare it to other common fan types.
| Feature | Squirrel Cage Fan (Forward-Curved Centrifugal) | Backward-Curved Centrifugal Fan | Axial Fan (Propeller Fan) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airflow Direction | In at the center, out at a 90° angle | In at the center, out at a 90° angle | Straight through, like a plane propeller |
| Pressure | Medium to high | High | Low |
| Efficiency | Good (50-70%) | Excellent (70-85%) | Varies, but generally lower for high-pressure jobs |
| Best For | HVAC systems, ducted ventilation, appliances | High-pressure industrial systems, clean air | Moving large volumes of air with little resistance (e.g., cooling fans, room fans) |
| Noise Level | Relatively quiet at low to medium speeds | Can be louder, especially at high speeds | Can be noisy, especially when moving air fast |
| Size | Compact for its output | Often larger for the same airflow | Can be very compact (like a computer fan) or very large |
Keeping Your Fan Happy: Simple Maintenance Tips
A little bit of care can dramatically extend the service life of your squirrel cage fan and keep its energy consumption low.
- Clean the Blades: The biggest enemy of a squirrel cage fan is dirt. A buildup of dust on the impeller can unbalance it, causing noise and vibration, and drastically reduce airflow. You should have your HVAC system professionally cleaned every few years. For smaller fans, like in a bathroom exhaust, you can often clean them yourself with a brush and vacuum.
- Check the Filter: In an HVAC system, a clogged filter is the most common cause of problems. It forces the furnace blower to work much harder, which wastes energy and can lead to motor burnout. Change your filter regularly!
- Listen for Trouble: If you hear new or unusual noises like squealing, grinding, or rattling, it could be a sign of a failing motor or worn-out bearing. Don’t ignore these sounds; call a professional.
- Inspect the Belt: If you have a belt drive system, check the belt for cracks or wear. A loose or worn belt can slip, reducing fan performance.
What’s That Noise? Troubleshooting Common Fan Issues
Is your system acting up? Before calling for service, you might be able to diagnose the issue. Here are some common problems:
- Problem: The fan is running, but very little air is coming out of the vents.
- Possible Causes: A severely clogged air filter, blocked ducts, or a very dirty squirrel cage impeller.
- Problem: The fan is making a loud rattling or thumping noise.
- Possible Causes: The impeller might be out of balance due to dirt buildup or a damaged blade. It could also be a loose mounting bolt.
- Problem: The fan won’t turn on at all.
- Possible Causes: This could be a simple tripped circuit breaker, a faulty thermostat, or a failed motor.
- Problem: The system is making a high-pitched squealing sound.
- Possible Causes: This often points to a worn-out motor bearing or a slipping belt on a belt-drive system.
The Future of Air Movement: What’s Next for Fans?
Fan technology continues to evolve, driven by the need for better energy efficiency and smarter control. Modern systems are increasingly using Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), which allow the fan’s motor to adjust its RPM precisely to match the heating or cooling demand. This saves a tremendous amount of energy compared to older fans that just run at full speed or not at all.
We’re also seeing the rise of smart fan systems that can be integrated with home automation. These systems can monitor air quality, humidity, and temperature, adjusting the air distribution for optimal comfort and efficiency. As part of the move toward green building technology, engineers are constantly refining impeller design and motor technology to squeeze every last bit of performance out of these essential devices, ensuring they meet strict AMCA standards for performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the main difference between a squirrel cage fan and a blower?
A: “Blower” is a general term often used for any fan that creates pressure. A squirrel cage fan is a specific type of blower, also known as a forward-curved centrifugal fan. So, all squirrel cage fans are blowers, but not all blowers are squirrel cage fans.
Q: Are squirrel cage fans energy efficient?
A: They are moderately efficient. While not as efficient as backward-curved centrifugal fans, they offer a great balance of cost, size, and performance for many common applications, especially in residential HVAC. Their efficiency drops significantly if they are not kept clean.
Q: Why is it called a squirrel cage?
A: It gets its name from the shape of its impeller, which has many small blades arranged in a circle, closely resembling an old-fashioned exercise wheel for a squirrel or hamster.
Q: Can you reverse a squirrel cage fan?
A: No. Unlike a simple axial fan, reversing the motor’s direction on a squirrel cage fan will not reverse the airflow. Because of the blade design and housing shape, it will still try to move air in the same direction, just very inefficiently.
Q: How do you clean a squirrel cage fan?
A: For an HVAC system, it’s best to hire a professional as it often requires specialized tools to access and clean the blower assembly safely. For smaller, accessible fans like a bathroom exhaust, you can usually remove a cover, take out the motor/impeller assembly, and clean the blades carefully with a stiff brush and vacuum. Always turn off the power at the circuit breaker first!
Key Takeaways
- A squirrel cage fan is a type of centrifugal fan used to move air in everything from your home furnace to industrial equipment.
- It gets its name from its impeller, which looks like a squirrel’s exercise wheel.
- It works by using centrifugal force to pull air into its center and throw it out at a 90-degree angle, building up pressure in the process.
- Its main advantage is its ability to work against high static pressure, making it perfect for systems with ductwork and filters.
- The primary components are the impeller, the motor, and the housing.
- Regular cleaning and maintenance, especially of the filter and impeller blades, are crucial for maintaining fan efficiency and preventing problems.